Laboratory
Migration and Mobility
At a Glance
Projects
Publications
Team
Project
Measuring and Modeling Cultural Distance Between Countries and Its Relationship with Migration Patterns
Carolina Coimbra Vieira, Sophie Lohmann, Emilio Zagheni; in Collaboration with Filipe Nunes Ribeiro (Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto, Minas Gerais, Brazil), Pedro Olmo Stancioli Vaz de Melo, Fabrício Benevenuto (both: Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil)
Detailed Description
Gravity-type models provide a classic framework for studying international migration. A key element in these models is the distance between countries because it affects the relative force of attraction between regions. The distance between two countries can be measured in a number of ways; for instance, by accounting for geographic, political, and socioeconomic factors, as well as language. Cultural distance is likely to be an important determinant of migration flows. However, measuring cultural distance has proven to be difficult, especially on a global scale. Digital trace data and, in particular, passively collected information from social media users offer new opportunities to map cultural distance between populations.
The main goals of this project are: (i) to measure distance between countries in terms of cultural preferences, (ii) to evaluate the extent to which cultural distance explains migration flows, and (iii) to assess the impact of migration on cultural preferences of the host population. Achieving these goals requires new data and methodological innovation, in particular in the context of developing metrics of cultural distance.
In a first paper, focusing mainly on developing methods, we used Facebook data from the Facebook advertising platform to evaluate and compare, in a statistical sense, the volume of interest in Brazilian cuisine around the world. Our results have revealed that similarities in culinary taste are often both a consequence and a predictive factor of migration flows.
Next, we refined the methods and tools for this project and scaled the data collection of digital traces to expand the geographic scope of the analysis beyond Brazil. While still focusing on food and drink as markers of a country’s culture, we measured the similarity between a set of 16 countries across the globe. We assessed the association between migration and cultural similarity between countries by comparing our measure of cultural similarity with international migration data. Our results have shown, among others, that larger immigrant populations are associated with more similar food and drink preferences between their country of origin and their country of destination.
A third study has illustrated the impact of adding these measures of cultural similarity (based on food and drink preferences) to gravity models used to predict migration. Our results have indicated that the new measure of similarity in food and drink preferences derived from Facebook data adds over and above standard explanatory variables in predicting migration, thus opening new opportunities to understand better the determinants of migration and improve migration predictions.
A Measure of Cultural Similarity Across Countries Based on Facebook Users’ Interests in Food and Drinks
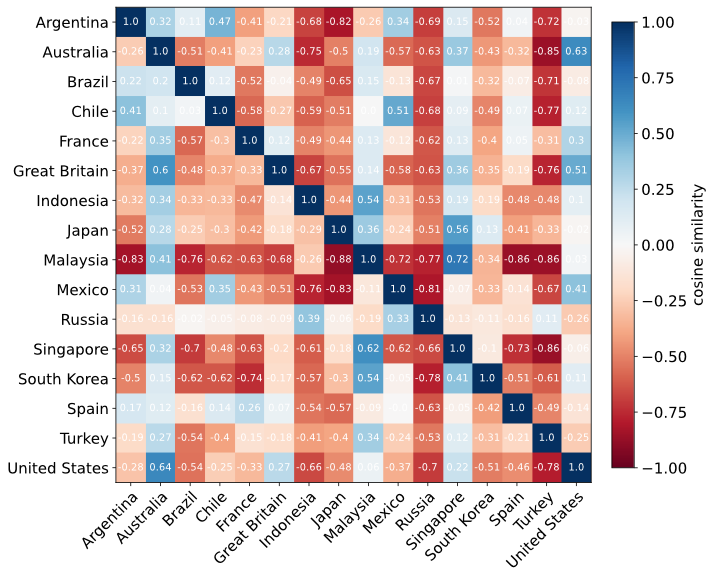
The plot shows our estimates of the asymmetric measure of cultural similarity between countries, based on Facebook users’ interests in food and drinks. Each cell corresponds to the index of similarity between the country in the row and the country in the column in terms of the number of Facebook users interested in each one of the top 50 foods and drinks preferred by the Facebook users living in the country in the row. © MPIDR; Source: COIMBRA VIEIRA, C.; LOHMANN, S.; ZAGHENI, E.; VAZ DE MELO, P. O. S.; BENEVENUTO, F.; RIBEIRO, F. N.: The interplay of migration and cultural similarity between countries: evidence from Facebook data on food and drink interests. PLoS One 17:2, e0262947-e0262947 (2022). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262947
Culture, International Migration, Ethnic Minorities, Migration, Psychology
Publications
Coimbra Vieira, C.; Lohmann, S.; Zagheni, E.:
Population and Development Review, 1–28. (2024)

Coimbra Vieira, C.; Lohmann, S.; Zagheni, E.; Vaz de Melo, P. O. S.; Benevenuto, F.; Ribeiro, F. N.:
PLOS One 17:2, e0262947–e0262947. (2022)

Coimbra Vieira, C.; Ribeiro, F. N.; Vaz de Melo, P. O. S.; Benevenuto, F.; Zagheni, E.:
In: WWW '20: proceedings of the Web Conference 2020; Apr 20-25, 2020, Taipei, Taiwan, 3091–3097. New York, NY: Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). (2020)
